What is satellite
What is satellite ? A satellite is something that orbits a larger object, that is, it orbits a planet in space. According to this definition, you might say that the Moon is a satellite. Yes, the Moon is indeed a satellite, but it’s a natural satellite. However, today we will learn about man-made satellites.
The moon is also a satellite, but it is a natural satellite. Inspired by this, scientists have created their own artificial satellites that orbit the Earth and play a very important role for us.
The size of a satellite depends on its function; it can range in size from that of a television to as large as a large truck. Satellites have solar panels on both sides that generate energy from sunlight.
How does a satellite work
There are two types of satellites: natural satellites and artificial satellites, which are created by humans. Artificial satellites are used for transmitting and receiving signals. Satellites orbit the Earth in its orbit. Satellites cannot be sent directly into space; they require the assistance of a rocket. The rocket carries the satellite to a very high altitude, approximately 3 to 36,000 kilometers, and then releases it into Earth’s orbit.
Satellites don’t require much power because there is no air or friction in space. Therefore, they use solar panels to generate energy from sunlight, and this energy powers their engines. The main function of a satellite is to receive and transmit signals, such as sending mobile and TV network signals, tracking GPS, and providing weather information. Predictions about rain, storms, and wind are all made using data from satellites. Satellites contain antennas that transmit video signals, cameras that send images of the Earth, and solar panels that generate power.
The difference between natural and artificial satellites.
What is the difference between natural and artificial satellites? A natural satellite is one that already exists, which we call the moon. Natural satellites orbit the Earth. Humans have no control over this type of satellite; that is, the moon does not send us any signals other than light. Natural satellites take a long time to complete an orbit around the Earth.
An artificial satellite is a man-made satellite that operates under human control. Like the moon, it orbits the Earth, but its orbital period is determined by humans. These satellites perform many functions for humanity, such as transmitting and receiving signals, and providing network services for phones and televisions. The first artificial satellite was Sputnik 1, which was built by the Soviet Union in 1957 and launched into space on October 4, 1957.
Satellite orbits
Our Earth has one natural satellite and several artificial satellites. These satellites revolve around the Earth. Satellites orbit at a constant speed and along a fixed path. When a natural or artificial satellite revolves around our Earth along a fixed path, that path is called an orbit. Different satellites are used for different purposes, and each satellite has a different orbit. The Earth has three main orbits.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO),
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO)
- Geostationary Orbit (GEO
The studios that create songs and videos send powerful signals through a ground station. Antennas on rooftops on Earth cannot receive these signals because they are not strong enough. However, the satellite’s powerful engine receives these signals and transmits them back to Earth. The satellite dish antennas on Earth easily pick up these signals, and they are displayed on televisions as video, song programs, etc. This is how the satellite receives signals and transmits them to areas on Earth.
Weather Monitoring satellite
Geostationary satellites are used for weather monitoring. These satellites orbit the Earth, gathering information about weather patterns, rainfall, storms, and hurricanes. While orbiting in Earth’s orbit, these satellites capture images of the Earth’s surface. These satellites are equipped with cameras and sensors, and the sensors are specially designed to detect cloud formations, rainfall, and temperature. Using these sensors, they gather information from sunlight and Earth’s temperature. Scientists use this information to predict when it will rain, what the Earth’s temperature will be, and to forecast storms, wind, humidity, and other weather phenomena. Benefit: This satellite provides accurate information in advance. The satellite’s camera is crucial, as it can scan the Earth even at such high speeds.
GPS satellite
The full form of GPS is Global Positioning System. These satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of 20,200 kilometers and transmit radio signals. The main function of these GPS satellites is to send signals to mobile devices on Earth. Through GPS, the exact location of any phone can be determined. This satellite system was created by the United States and consists of a constellation of 24 satellites that work together to send signals to different parts of the Earth. These satellites are controlled by a large scientific organization called a ground station. We can see locations on Google Maps through these satellites, and mobile phones and other devices are tracked using these same satellites.
What are the different parts of a satellite?
- power system: The satellite generates its energy from sunlight through its power system.
- battery: They store solar energy in batteries and use the batteries when there is no sunlight.
- Communication System: It receives commands from Earth and sends them back to Earth as signals.
- Payload: The payload contains cameras and sensors. The camera takes pictures of the Earth, and the sensors monitor the weather:
- Propulsion System: Changing the satellite from one operator to another or changing the satellite’s position.
- Thermal Control System: This protects the satellite from extreme temperature fluctuations and maintains a consistent temperature.
- Command & Data Handling System: It is also called the brain of the satellite. It contains both software and hardware that execute the commands given from Earth correctly.
Why don’t satellites fall to Earth
The Earth has gravity, which pulls any object towards it. A satellite cannot fall to Earth because its speed is so great that it prevents the Earth’s gravitational force from overpowering it. The balance between the Earth’s gravity and the satellite’s orbital speed keeps the satellite in orbit, preventing it from falling to Earth. This is because the satellite is constantly moving at a high speed. If the satellite’s speed were to slow down, it would leave its orbit and be pulled towards the Earth due to the Earth’s gravity.
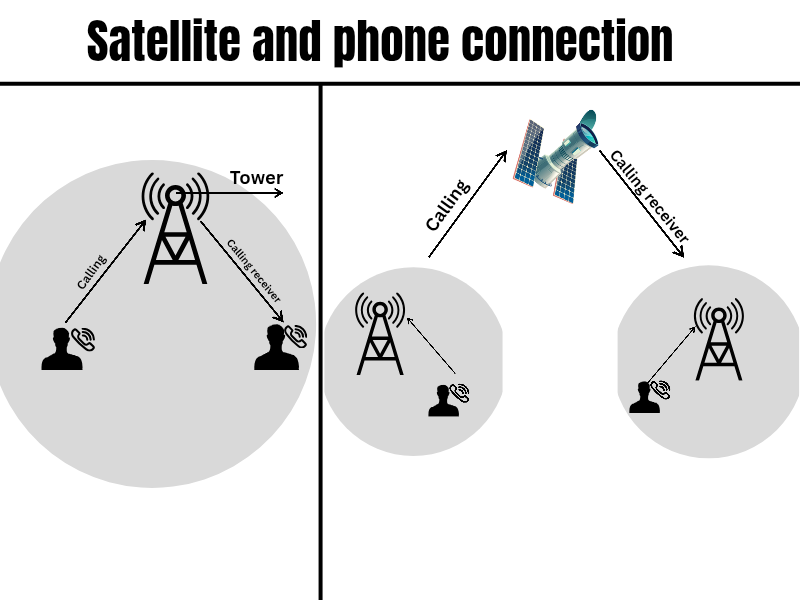
Satellite signal connection
How does a satellite connect to a phone, device, or TV channel? The connection method varies for different devices. A satellite connects via radio waves to an antenna on the satellite. Inside the satellite is a transponder that receives signals from Earth, amplifies them, and then transmits them back to a dish or tower on Earth. The satellite’s connection speed is as fast as the speed of light, approximately 300,000 kilometers per second.
Where is the satellite getting its internet connection from?
There is no internet inside a satellite, nor is there internet in space. Satellites receive their internet connection from satellite connection centers, or ground stations, located on Earth. These ground stations transmit the internet to the satellites via radio signals.
What is internet